The IT Leader's Definitive Guide to Predictive Modeling
This post was first published on Plutora’s blog
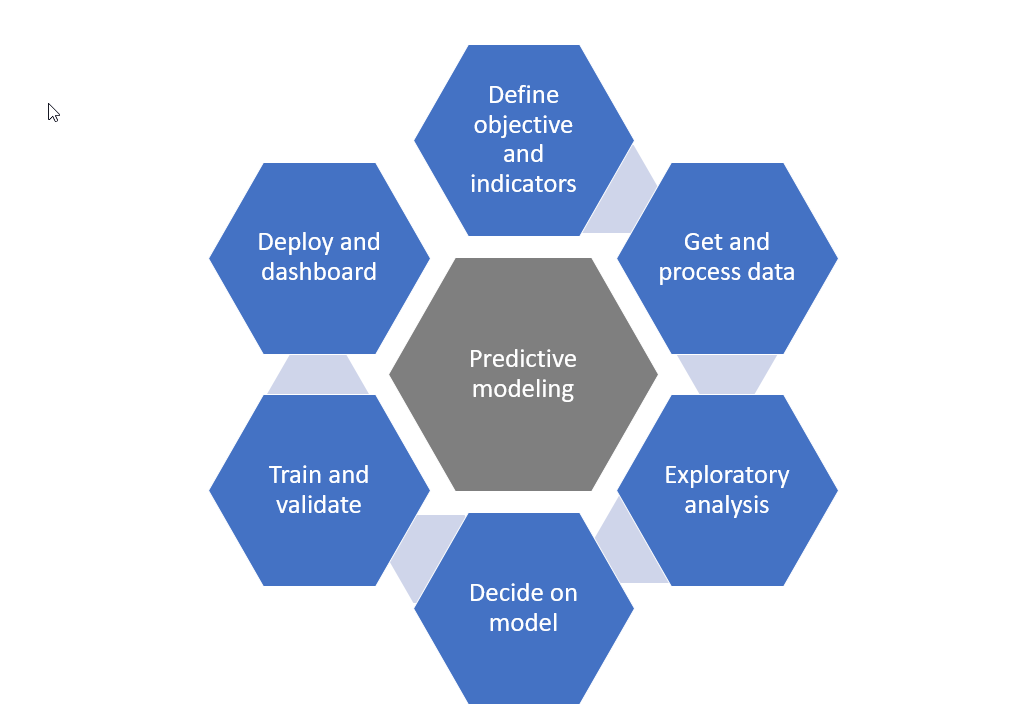
Whether you’re new to predictive modeling or just need a refresher, this post will walk you through the essential steps of predictive analysis. Predictive analysis starts from your business objective. After determining that, I’ll look at how to get and explore the data. Then, once the data is clean and ready to go, I’ll take you through deciding on a model and assessing whether it is any good. If those model metrics look OK, it’s time to deploy, monitor, and iterate. Finally, take action and involve your end-user by creating a dashboard to track performance. But before diving in, let’s cover what predictive analytics is and why you need it.
What Is Predictive Modeling?
Predictive analytics is the process of using measurable indicators to show relationships between data points, as well as modeling these relationships to predict outcomes. Its uses in business are many. To name a few benefits, predictive analysis
- Can detect or prevent problems, such as identifying bottlenecks in production.
- Helps you spot patterns that could indicate fraud or security breaches.
- Assists you with decision making by tracking releases or suggesting the best product for a client based on their previous purchases.
- Can be leveraged to streamline services. For example, showing expected service usage can help you plan when and where you need extra resources.
The value of predictive analytics is clear: Understand your market or service delivery pipeline better, detect problems early, and use your resources to their fullest potential. And to get the best value out of your predictive analytics, you should start by knowing exactly what your objective is.
Step 1: Identify Your Business Objective
What does your business objective have to do with modeling? Everything. Really, everything.
Without knowing your business objective, you can easily get bogged down in an endless cycle of data gathering and exploratory analysis. While this can be fun (if that’s your sort of thing), it’s wasteful and goes against lean principles.
So, define your goal and make sure it’s measurable and adds value to your business. Whether it’s tracking which projects take the longest from start to delivery or analyzing the characteristics of your customer base, know exactly what you want to achieve before starting out.
Step 2: Identify the Key Indicators
Now that you know what you want to track, you need to know how to track it. This may be time to completion, number of jobs completed, or prices of goods over time—whatever is important to your objective.
Ask yourself: How is the indicator measured? This question is important, as it will determine how you format the data and which method of analysis you choose. Where does the data live? Is it accessible and easy to extract? If the data only exists in a file drawer, you may need other data sources.
It’s not only about what you have, but also about what you don’t have. What’s missing? To quote statistician John Tukey, “The combination of some data and an aching desire for an answer does not ensure that a reasonable answer can be extracted from a given body of data.” Sometimes you may identify indicators that you don’t have at present and will need to incorporate into your data collection. Don’t stress, it’s an iterative process.
Step 3: Get the Data
Now the fun starts. The specifics here depend on where your data lives, but the objective is the same: Get your data into a workable form.
This step may entail getting the data via API calls, working some SQL magic, or just phoning a colleague to get that spreadsheet. If you’re deciding on a database, consider the volume of data and how easy it is to scale the database. Nowadays, the availability and affordability of cloud computing makes scaling easier—just fire up some new nodes.
Decide on the data you need and integrate those data sources. Especially when working with big data, you don’t want to be slowed down by unnecessary information. Make sure you have what you need, and no more.
You’re also likely to have two sources of data: historical and new. You’ll use historical data to train the algorithm, or model. Afterward, you can use new data to make predictions and assess the quality of the algorithm. Many companies keep these data sources separate, but you can use filters to get the information you need if the data is in the same database. Once you have the data, you can start cleaning and analyzing.
Step 4: Process the Data
This step inevitably takes up 80% of the time spent on analysis. Make sure your features of interest are in the format you want.
Formatting Matters
Depending on your model and software, you might want your data in a long format (one feature per column) or wide format (one row per observation). Some software requires time series data to be in wide format, with one row per observation, whereas others advocate for long format data as the tidiest approach.
Here’s some flight delay data in both long and wide format:

Convert and Standardize
You may also need to manipulate features to have them the way you want, such as converting minutes to hours or changing a variable such as income to log format.
 The relationship between salary and age, before (left) and after (right) log-transforming salary. The data on the right form a straight-line relationship, which is just the way we need it to be for linear models.
The relationship between salary and age, before (left) and after (right) log-transforming salary. The data on the right form a straight-line relationship, which is just the way we need it to be for linear models.
Make sure your feature names are standardized. You don’t want to deal with columns alternately called Gender, Sex and Male. You’ll pull your hair out trying to find what you are looking for!
Have a Workflow
Keep your clean data separate from your raw data. And never, ever save over your original data. You never know when you’ve made a mistake or missed something in your data processing. You always want to be able to go back and check that the data processing was done correctly. Consider version control, not just for the code used for your analytics but also of the data itself.
Whatever your process, have a workflow. Just as with software engineering, you want all of your analytics steps to be repeatable. In other words, all changes should be defined in code and someone else should be able to replicate it on their machine.
This is where a workflow management tool or value stream management platform comes in handy. You get visibility and automation of the tasks for the whole team to see. You can also connect various low-level productivity and deployment tools such as Jira, GitHub, and Jenkins on a single platform.
Step 5: Exploratory Analysis
At this stage, you’ll want to get to know your data well. How many observations are there? How many missing values are there? Is there some pattern to the missing data? Data that is not randomly missing could be a problem later. If all metrics from a certain department are missing, we can’t predict anything about that department’s performance, now can we?
Visualize, Visualize, Visualize
A good graph makes it much easier to spot trends and unusual or outlying values. Take note of these unusual values. Sometimes it’s a mistake (Oops! Someone entered 333 instead of 33!). Sometimes it’s a subgroup that’s in some way different from the main group. For example, retirees may not interact with a website in the same way that younger customers do. Either way, you’ll want to take note of these values and, if appropriate, act.
Get Descriptive
You can take your observations further by getting averages, deviations from the mean, and, if relevant, correlations between indicators (is shorter time to completion associated with reduced output quality?). Having an idea of the state of affairs—even before any modeling is done—is often very useful in itself.
Within the software industry, you may want to see the deployment frequency or the lead time for changes. This can already give you insights into where problems occur and where you are spending time or money. However, you may want to take your analytics one step further by creating models to predict future events.
Step 6: Decide on the Right Model to Use
Now that the data is in the format you want and you’ve looked at patterns in the data, the model building can start! Hooray, you’ve made it! Review your business objective. For example, do you want to see differences between groups (as in the case of A/B testing) or relationships between features? Perhaps you want to group features based on their similarities.
Each of these objectives lend themselves to a different type of model. Some of the most common model categories are
- Classification
- Regression
- Clustering
- Time-series forecasting
- Neural networks
Model Types
Classification
Classification models, such as decisions trees or logistic regression, work when the outcome is a category. Predict complete versus incomplete tasks, or classify an image as a cat, dog, or llama. Predicting customer churn is another common application of these types of models.
Regression
Regression models, such as linear regression and decision tree regression, are used when the outcome is a number. An example is hours spent on a task or the number of tests passed on the first run.
In addition to considering whether your outcome (or target) variable is categorical, look at whether any features are categorical. This can help you decide whether a regression model or decision tree regression is best, or whether you should use something else entirely.
If only a few features are categorical and they only have a few categories, you can one hot encode your categories so that each category becomes its own column. You can now use these one-hot-encoded features instead of the original feature in a regression-type model. But if you have very many features or features with many categories, one hot encoding won’t work well. In this scenario, models that can handle categorical features, such as tree-based models and neural networks, are the best choice.
Clustering
Clustering models group similar data points together and can be used to identify people with similar tastes or spending habits. You can also group actions that are likely to occur together. For example, you can use these to distinguish between fraudulent and real transactions. The most common clustering method is k-means clustering, though this isn’t the only method.
Time-Series Forecasting
Time-series models take changes in time into account and are used to predict changes in, for example, stock market prices or traffic congestion.
Neural Networks
Neural networks can predict outcomes that are not linearly related to features. These models are used in geospatial analysis, natural language processing, and image recognition, to name a few areas. The upside of neural networks is that they can do nearly anything. The downside is that they require a lot of data. They are also “black boxes” in the sense that you don’t know which features are most influential in predicting the outcome.
Going Beyond a Single Model
In many cases, you may want to try several models to see what works best. You can also use models consecutively. For example, first cluster similar observations and then use these clusters in a classification model. Or, combine predictions from different models.
Step 7: Train Your Model
Once you’ve decided on the right model, split the data into a training and a test set. Train the model on the training data set. Once you are happy with the accuracy of the model, you can assess whether it generalizes to other data by checking the model accuracy on unseen data—the test set. Usually, roughly 80% of the data is used for training and 20% for testing. Other splits are, of course, also possible. A 70-30 split is also popular.
Step 8: Validate Your Model
The important questions to ask in this step are whether your model generalizes well to new data and whether it meets your performance targets.
Does the Model Work on New Data?
Use the model you built on the training set to predict the target outcome on the test set. This step is crucial because this is where you can see whether you are overfitting the data. Overfitting is when the model is too sensitive to the data; the model predicts tiny changes in the training data but performs poorly on the test data.
Luckily, this is easy to spot. If your model accuracy on the test data is much lower than on the training data, the algorithm has been overfit.
Less often a problem, but also possible, is underfitting. In this case, the model is not sensitive enough to changes in the data points. Create a more complex model, add more data, augment your data with other sources, or train the model for longer (i.e. include more epochs, or number of runs, when training your neural network).
Is the Model Acceptable to Use?
One more thing: If you’re making predictions about an event, you’ll need to know when to stop. What defines success? Is it 90% accuracy? If you have a classification problem, is it achieving certain precision or recall scores?
The definition of success is business-specific. You need to decide for yourself what’s important.
For one business, reducing false positive results may be very important. After all, you don’t want to tell someone that they have cancer when, in fact, they don’t. For others, reducing false negatives may be the key objective. It’s better to be alerted to something that may not happen, like an earthquake, than to ignore a potentially risky situation.
Once you’re happy with your model, you can go ahead and put it into production.
Step 9: Deploy and Dashboard
To act on your newly gained insights, you need to get the data into the hands of the right people. Integrate your model into your business intelligence platform or build your own.
A dashboard that refreshes at a suitable rate is a great way to monitor the state of the system. For example, Plutora has a cloud-based analytics platform that assists companies with release, scope, environment, and deployment management.
You can also integrate your model into the day-to-day operation of your business. Set up automated alerts if certain conditions are met, such as identifying a security concern, possible downtime, or a customer who is likely to leave. In call centers, predictive models are routinely used to carry out intelligent call routing, profile customers, and provide a better customer experience.
Regularly monitor how well the model is working. You don’t want unexpected surprises here (think self-driving cars gone rogue and gender-biased recruitment models). As you put the model into practice, its performance may go down with time, so remember to check for obsolete models.
And as you go along, document the process. Your colleagues and your future self will thank you when you are trying to remember exactly why you decided on those specific metrics or why you chose to change a model.
Wrapping Up
Predictive analytics can increase revenue and reduce loss by identifying problems early. Use it to spot trends, streamline services, or increase sales.
Starting from your business objective, identify key indicators that are measurable in the data.
Train and test your algorithm on historical data, and then monitor how well it predicts future data. These steps may require several iterations to get it right; you may add more data sources as you know what’s important or where you have gaps and inaccuracies in the data.
Finally, get it into the hands of the user so that you can take action. Make sure your implementation addresses the needs of the user and is easy to use.
Well done! This is just the start. Analytics is an ongoing process. Now that you’re here, examine your regular reports. What can you improve? Have new questions come up since adding new analyses? What new decisions will you take, and how can you monitor that they are improving your business? And if you are not yet monitoring your key performance indicators, what are you waiting for?